In precision metering and fluid-handling systems, gear pump repeatability is essential for maintaining accurate, consistent flow rates. Whether you’re dosing chemicals, transferring lubricants, or handling process fluids, repeatability determines how reliably a pump performs under identical conditions.
According to Micropump, repeatability depends on how well a pump maintains its output despite internal “slip” — the unavoidable backflow through clearances within the pump. Understanding and controlling this slip is key to achieving predictable performance.
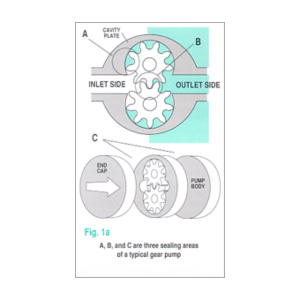
What Causes Slip in Gear Pumps?
Slip, or back leakage, occurs because small clearances are necessary between moving parts. These clearances allow gears to rotate freely but also let some fluid leak from the outlet back to the inlet, lowering actual flow.
Micropump identifies three main sealing zones in rotary gear pumps where slip can occur:
- Between gear tooth tips and the pump cavity wall.
- At the gear mesh where teeth engage.
- Along the faces of gears, the housing, and the end cover.
Even with precision machining, some degree of slip is inevitable — and understanding how it changes under different conditions is crucial to improving repeatability.
Factors Affecting Gear Pump Repeatability
1. Differential Pressure
As differential pressure increases, so does slip. The higher pressure forces more fluid through the clearances, reducing net flow.
Some advanced designs, such as suction-shoe-style pumps, counter this by using pressure to enhance the seal, tightening clearances automatically and minimizing slip at high pressures.
2. Fluid Properties
Viscosity: Thicker (more viscous) fluids reduce slip since they resist flowing through tight gaps.
Shear Behavior: Non-Newtonian fluids (whose viscosity changes with shear rate) can introduce unpredictable slip patterns.
Phase Composition: Fluids containing gas, bubbles, or slugs cause erratic slip behavior, decreasing repeatability.
3. Design Precision & Wear
Small manufacturing variations or wear over time increase clearances and thus slip. Even two identical pumps can show slight flow differences due to tolerance variation. Over time, this wear affects repeatability.
How to Improve Gear Pump Repeatability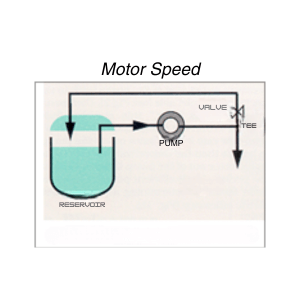
- Use Closed-Loop Fluid Sensing
Integrate sensors that measure flow, viscosity, or temperature. Use feedback to automatically adjust pump speed and maintain target flow despite slip variations.
- Add a Mechanical Bypass Loop
A bypass leg downstream of the pump can stabilize flow by diverting a controlled amount back to the reservoir. This simple adjustment smooths out minor fluctuations.
- Control Motor Speed Precisely
Because gear pumps are positive displacement, flow output is proportional to speed. Maintaining steady motor speed — or compensating dynamically through electronic controls — is one of the most effective ways to achieve repeatable flow.
Running at higher speeds (within design limits) also helps because slip becomes a smaller percentage of total flow, improving overall repeatability.
Summary: Making Gear Pumps Consistent and Reliable
Repeatability is the difference between a good pump and a truly precise one. To achieve reliable performance:
- Select pump designs with pressure-responsive sealing.
- Keep mechanical tolerances tight and monitor wear.
- Use smart sensors or motor control systems.
- Operate near the upper speed range when possible.
By combining mechanical precision with intelligent control, engineers can dramatically improve gear pump repeatability — reducing waste, downtime, and maintenance costs across critical fluid systems.
Source: Adapted from technical information by Micropump.

